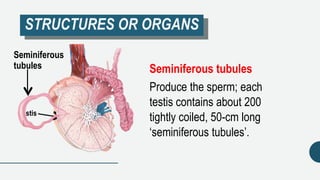
43 reproductive system bioninja
6.6 Reproduction | BioNinja Follicular Phase: FSH stimulates growth of several follicles Dominant follicle secretes estrogen Estrogen inhibits growth of other follicles (and FSH) Estrogen stimulates development of endometrium Ovulation: A surge in LH causes ovulation (egg release) Rupturing of follicle creates a corpus luteum Luteal Phase: Menstrual Cycle | BioNinja pituitary hormones The menstrual cycle describes recurring changes that occur within the female reproductive system to make pregnancy possible Each menstrual cycle lasts roughly one month (~28 days) and begins at puberty (menarche) before ending with menopause There are two key groups of hormones which control and coordinate the menstrual cycle:
11.4 Sexual Reproduction | BioNinja 11.4 Sexual Reproduction | BioNinja Sexual reproduction involves the development and fusion of haploid gametes Brent Cornell Site Navigation[Skip] Home Course Outline Assessment PSOW Command Terms Standard Level 1: Cell Biology 1. Cell Introduction 2. Cell Structure 3. Membrane Structure 4. Membrane Transport 5. Origin of Cells 6. Cell Division

Reproductive system bioninja
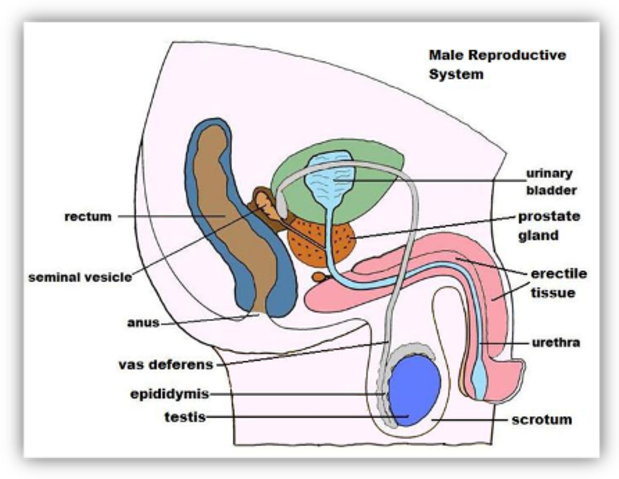
Male Reproductive System | BioNinja The male reproductive system includes all the organs responsible for the production of sperm (the male gamete) It also includes the organs that are involved in synthesising the semen in which the sperm is transported during copulation Male Reproductive System (Front View) ⇒ Click on the diagram to show / hide labels Topic 6.6: ReProduCTIve SySTEmS - BioNinja Reproductive Theories One of the earliest theories involving how human reproduction occurs was the ‘soil and seed’ theory proposed by Aristotle • Males provide all the information for life in a ‘seed’, which forms an egg when mixed with menstrual blood (the ‘soil’) Female Reproductive System | BioNinja The female reproductive system includes all the organs responsible for the production of an oocyte (the female gamete) It also includes the organs involved in initially developing and maintaining an embryo during the early stages of pregnancy Female Reproductive System (Front View) ⇒ Click on the diagram to show / hide labels
Reproductive system bioninja. 6.6 Hormones, Homeostasis and Reproduction | BioNinja 6.6 Hormones, Homeostasis and Reproduction | BioNinja Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed Brent Cornell Site Navigation[Skip] Home Course Outline Assessment PSOW Command Terms Standard Level 1: Cell Biology 1. Cell Introduction 2. Cell Structure 3. Membrane Structure 4. Membrane Transport 5. Origin of Cells 6. Cell Division Female Reproductive System | BioNinja The female reproductive system includes all the organs responsible for the production of an oocyte (the female gamete) It also includes the organs involved in initially developing and maintaining an embryo during the early stages of pregnancy Female Reproductive System (Front View) ⇒ Click on the diagram to show / hide labels Topic 6.6: ReProduCTIve SySTEmS - BioNinja Reproductive Theories One of the earliest theories involving how human reproduction occurs was the ‘soil and seed’ theory proposed by Aristotle • Males provide all the information for life in a ‘seed’, which forms an egg when mixed with menstrual blood (the ‘soil’) Male Reproductive System | BioNinja The male reproductive system includes all the organs responsible for the production of sperm (the male gamete) It also includes the organs that are involved in synthesising the semen in which the sperm is transported during copulation Male Reproductive System (Front View) ⇒ Click on the diagram to show / hide labels
































Post a Comment for "43 reproductive system bioninja"